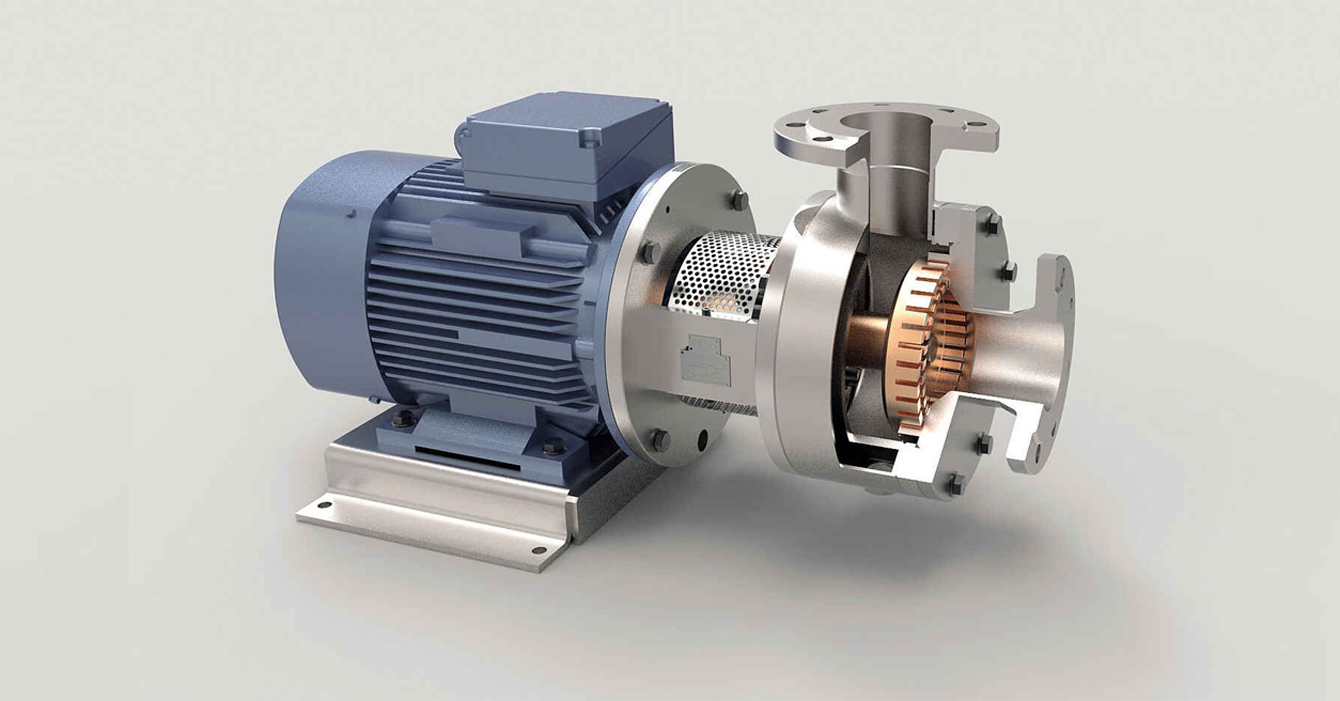
Homogenizer — equipment is designed to grind, evenly distribute and mix particles in liquid and semi-solid media. The main purpose of using homogenisers is to obtain a stable and homogeneous mixture that does not delaminate over time. Homogenisation is based on creating high pressure and passing the liquid through a narrow gap between valves or plungers. In the process, the particles are destroyed or evenly distributed in the medium.
- High pressure:
The liquid is pumped in under high pressure (up to 1500 bar). - Cavitation and shear forces:
The fluid flow passes through the homogenising unit, where a combination of forces acts: pressure, cavitation, shear and impact loads. - Grinding of particles:
The particles are broken down to micro- or nano-size to form a homogeneous mixture. - Even distribution:
The resulting mixture remains stable and does not tend to delaminate.
Areas of application
- Food industry:
- Homogenisation of milk, cream, yoghurt, sauces, juices, purees.
- Creating stable emulsions such as mayonnaise or ice cream.
- Pharmaceuticals:
- Preparation of dosage forms: syrups, suspensions, emulsions, vaccines.
- Ensuring an even distribution of active ingredients in the preparation.
- Cosmetics industry:
- Production of creams, lotions and shampoos.
- Formation of emulsions with a fine texture.
- Chemical industry:
- Dispersion of pigments, paints, adhesives, varnishes.
- Working with polymer solutions and suspensions.
- Biotechnology:
- Dissection of cells and isolation of intracellular components (e.g. proteins or enzymes).
Types of homogenisers
- High-pressure homogenisers:
They are used for handling large volumes of product and high pressures.- Areas of application: dairy industry, pharmaceuticals.
- Rotary-stator homogenisers:
The mixing process is driven by the interaction of the rotor and stator, which generate high shear forces.- Areas of application: cosmetics, chemical processes.
- Ultrasonic homogenisers:
They operate on the principle of cavitation created by ultrasonic waves.- Areas of application: biotechnology, laboratory research.
Features of homogenisers
- Grinding to nanoscale:
The ability to reduce particles to 0.1 micron in size to ensure a consistent product texture. - Uniformity:
Ensure uniformity even in complex multi-component systems. - Compatible with various liquids:
They work with low- and high-viscosity media. - Hygienic:
Most models are made of stainless steel that meets hygiene standards (FDA, EHEDG). - Automation:
Possibility of integration into automated production lines. - Energy efficiency:
Modern homogenisers consume less energy thanks to advanced designs.
How to choose the right homogenizer?
- Product type:
Determine whether an emulsion, dispersion or homogenisation is required. - Pressure level:
Choose equipment that can provide the necessary pressure to achieve the desired particle size. - Productivity:
Consider the volume of product to be processed per unit of time. - Compatible with liquids:
Select a model that matches the fluid characteristics (viscosity, temperature, chemical composition). - Materials:
For aggressive or sterile environments, choose models made of AISI 316L stainless steel. - Additional features:
- Compatible with CIP/SIP systems.
- Availability of automatic settings and monitoring systems.