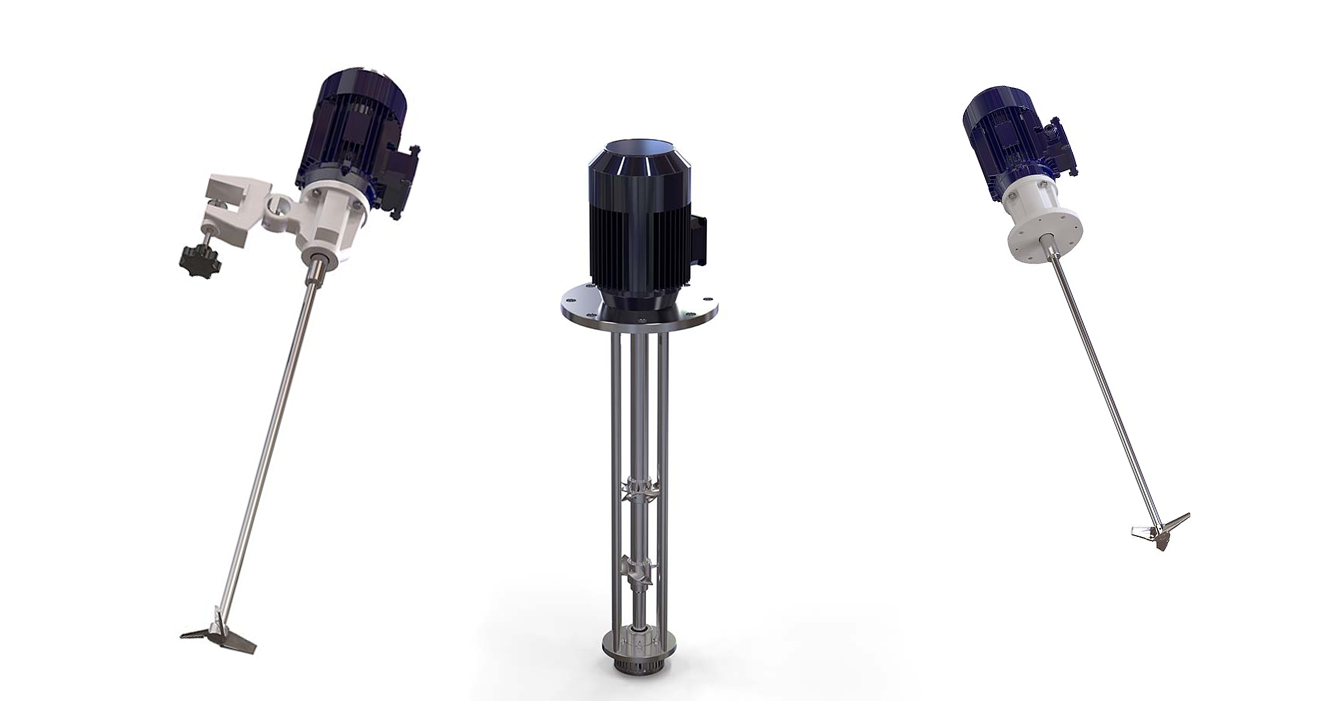
An agitator is a device designed to mix, emulsify, homogenise or disperse liquids and semi-solids. Due to their design and functionality, agitator mixers are widely used in various industries.
The agitator-mixer consists of an electric motor, a drive and a mixing element (blade, propeller, turbine) that rotates inside the tank. The movement of the mixing element creates a hydrodynamic flow that ensures uniform mixing of the components.
The process can take place through various mechanisms:
- Mechanical mixing: Blades or propellers create turbulent flow in the liquid.
- Dispersion: The particles are divided into smaller fractions.
- Emulsification: Mixing two phases, such as water and oil, to form an emulsion.
- Homogenisation: Reducing the particle size to produce a homogeneous product.
Areas of application
- Food industry:
- Mixing sauces, creams, yoghurts, syrups.
- Preparation of emulsions (e.g. mayonnaise).
- Pharmaceuticals:
- Homogenisation of creams, ointments, suspensions.
- Preparation of sterile solutions.
- Cosmetics industry:
- Mixing creams, shampoos, gels.
- Create emulsions and gel-like textures.
- Chemical industry:
- Dispersion of paints, varnishes and adhesives.
- Mixing aggressive and viscous liquids.
- Agriculture:
- Preparation of feed mixtures.
- Dissolving fertilisers and pesticides.
Features of the agitator mixers
- Type of mixing element:
- Paddle stirrers for viscous liquids.
- Turbine agitators for low-viscosity applications.
- Propeller agitators to create a strong flow.
- Materials of execution:
- Stainless steel (AISI 304/316) for food, pharmaceutical and chemical products.
- Corrosion-resistant coatings for use with aggressive substances.
- Type of drive:
- Electric: Ensures high performance and stability.
- Pneumatic: For use in explosive atmospheres.
- Rotation speed:
The adjustable speed allows the agitator to be adapted to different processes (homogenisation, mixing, emulsification). - Possibility of integration:
Some models support automation and integration into production lines.
What is the right mixer for you?
- Process type:
Determine whether the stirrer is used for mixing, emulsifying, dispersing or homogenising. - Fluid characteristics:
- Viscosity: Consider whether the medium is liquid, viscous, or paste-like.
- Sensitivity: Whether the structure of the product needs to be preserved.
- Tank volume:
Choose the model with the right shaft length and power for your tank. - Materials:
Select the material of the body and mixing element depending on the medium (food, aggressive or sterile liquids). - Compatible with CIP/SIP systems:
For pharmaceuticals and food processing, make sure the equipment supports automatic cleaning. - Rotation speed:
Choose a model with adjustable speed if you need to perform different tasks. - Energy consumption:
Consider equipment efficiency to reduce energy costs.