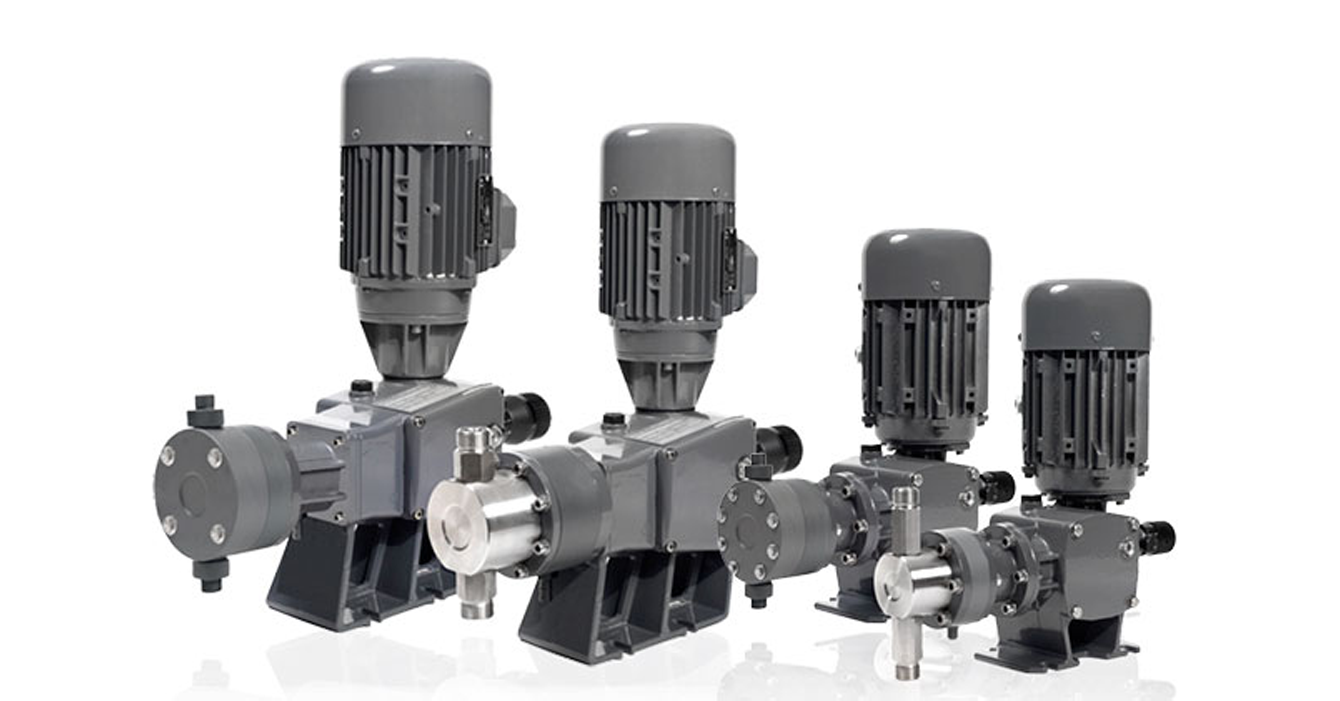
The plunger pump works on the principle of creating pressure in the chamber due to the translational movement of the plunger (piston). Main stages of operation:
- Reverse plunger stroke:
As the plunger reciprocates, a vacuum is created in the working chamber, which draws the liquid through the inlet valve. - Straight plunger stroke:
As the plunger moves forward, the fluid is compressed, creating pressure, and is discharged into the outlet pipe through the outlet valve. - Valve system:
One-way valves allow fluid to flow in one direction only, preventing reverse flow.
Areas of application
- Chemical industry:
- Transportation of aggressive substances such as acids, alkalis, solvents.
- Precise dosing of reagents in chemical processes.
- Pharmaceutical industry:
- Highly accurate dosage of active ingredients in the production of medicines.
- Sterile transport of liquids in laboratory or production environments.
- Energy:
- Supply of fuel, lubricants and coolants.
- Use in high-temperature or high-pressure systems.
- Oil and gas industry:
- Pumping heavy oil products and liquids with high viscosity.
- Introduction of chemical additives in the refining process.
- Food industry:
- Precise dosage of syrups, flavours and preservatives.
- Working with viscous products such as honey or pastes.
Features of plunger pumps
- High pressure:
Plunger pumps can deliver pressures of up to 1000 bar, enabling the transport of liquids even in difficult conditions. - Dosing accuracy:
They provide precise control of fluid flow, even in small volumes, making them ideal for applications requiring high repeatability. - Resistance to aggressive environments:
The use of materials that are resistant to chemical attack (stainless steel, titanium, ceramics) allows us to work with aggressive liquids. - Simplicity of design:
The robust and compact design with a minimum of moving parts ensures durability and reduces maintenance costs. - Wide viscosity range:
They can transport both watery and highly viscous liquids. - Performance control:
You can adjust the fluid flow rate manually or automatically.
How do I choose the right plunger pump?
- Fluid characteristics:
- Take into account the viscosity, chemical composition and temperature of the liquid.
- Check whether the liquid is aggressive or abrasive.
- Performance and pressure:
- Determine the required volume of fluid to be delivered per unit time.
- Make sure that the pump meets the maximum pressure requirements.
- Materials of execution:
- For aggressive liquids, choose models with a body and plunger made of chemically resistant materials (e.g. PTFE, ceramic).
- Operating conditions:
- Consider the temperature, humidity and the need to work in explosive atmospheres.
- Protection systems:
- Make sure that the pump is equipped with a dry-running or overpressure protection system.
- Sanitary requirements:
- For the food or pharmaceutical industry, check the compliance of the pumps with FDA or EHEDG standards.