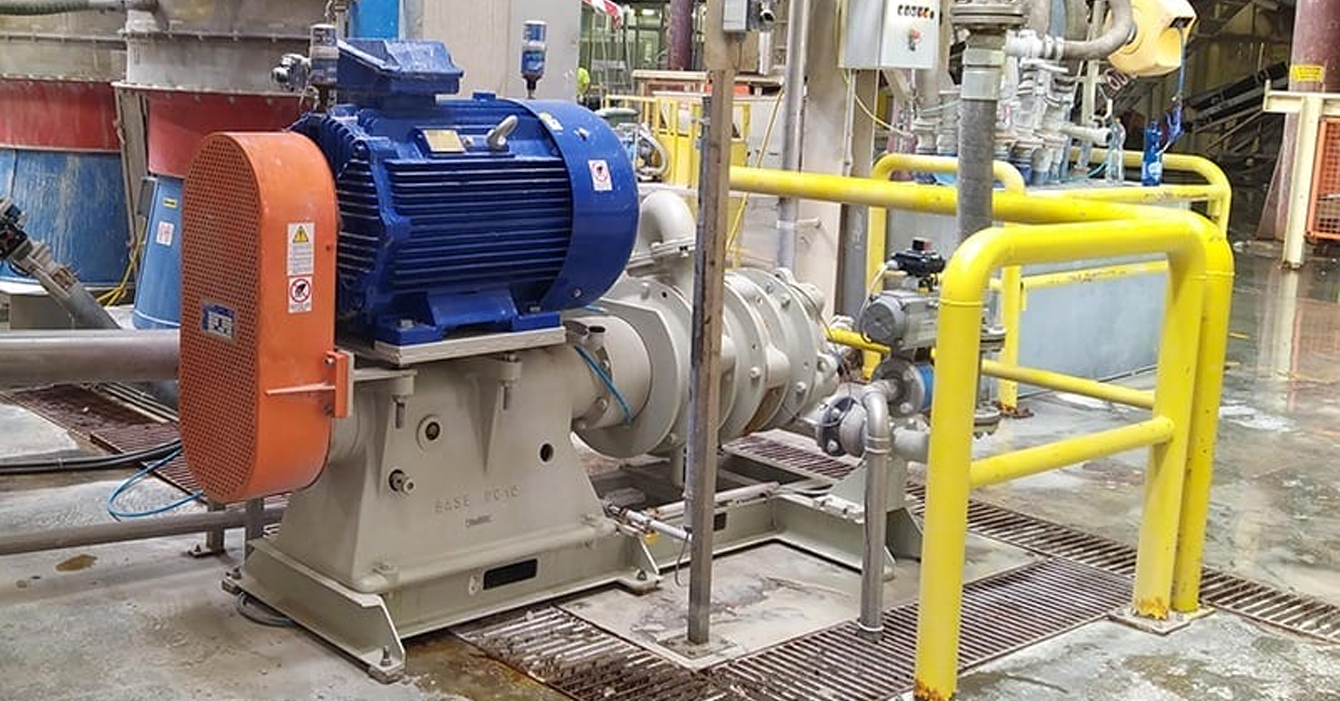
Slurry pumps operate on the basis of a piston, rotary or centrifugal mechanism adapted to work with a high solids content in the liquid. An important characteristic of slurry pumps is their large working channels, which prevent clogging and ensure unimpeded transportation of substances.
Application of slurry pumps
- Mining industry: They are used for pumping slurries, pulps, ore concentrates and tailings.
- Construction: Efficiently transport concrete mixtures, mortars and abrasive building materials.
- Energy: They are used to pump ash slurries, sludge and other by-products of power plants.
- Metallurgy: They provide transportation of molten slag, production waste and thick chemical mixtures.
- Wastewater treatment: They are used for pumping sludge, sludge and contaminated liquids.
- Pulp and paper industry: They are used for handling slurries, saturated fibers, and sludges after treatment.
Features of slurry pumps
- Resistance to abrasive media: Thanks to the use of special wear-resistant materials such as rubber, polyurethane or high-strength steel, the pumps work efficiently with solid particles.
- Large working channels: The design allows pumping liquids with a high solids content without the risk of blockage.
- “Heating shirt": Some models have a heating system for working with liquids that can solidify or change their properties at low temperatures.
- Working in difficult conditions: The pumps are specially adapted for high pressure, temperature and contamination.
- Self-suction: Many models are able to operate without preliminary filling with liquid, which simplifies their startup.
How to choose a slurry pump
- Fluid characteristics. Determine the viscosity, abrasiveness, and presence of solid inclusions.
- Productivity. Calculate the required pumping volume per unit of time.
- Material. Select a pump made of materials that are suitable for the operating conditions (e.g. corrosion and abrasion resistant).
- Working conditions. Consider temperature, pressure, and the need for a “heating jacket.”
- The complexity of maintenance. Choose models with easily accessible components for maintenance and repair.